



suivant: Intersection of a 2D
monter: Graph of a line
précédent: Tangent to a 2D
Table des matières
Index
Tangent to a 2D graph : tangent
See also : ![[*]](crossref.png) for plane geometry and
for plane geometry and
![[*]](crossref.png) for 3D geometry.
for 3D geometry.
tangent takes two arguments : an geometric object and a point
A.
tangent draws tangent(s) to this geometric object crossing through
A. If the geometric object is the graph G of a 2D function,
the second argument is either, a real number x0, or a
point A on G. In that case tangent draws a tangent to this
graph G crossing through the point A or through the
point of abscissa x0.
For example, define the function g
g(x):=x^2
then the graph G={(x,y)
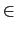
 2, y=g(x)}
of g and a point A on the graph G:
2, y=g(x)}
of g and a point A on the graph G:
G:=plotfunc(g(x),x);
A:=point(1.2,g(1.2));
If we want to draw the tangent at the point A to the graph G, we will input:
T:=tangent(G, A)
or :
T:=tangent(G, 1.2)
For the equation of the tangent line, input :
equation(T)




suivant: Intersection of a 2D
monter: Graph of a line
précédent: Tangent to a 2D
Table des matières
Index
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse
![[*]](crossref.png) for plane geometry and
for plane geometry and
![[*]](crossref.png) for 3D geometry.
for 3D geometry.