



suivant: Rational function given by
monter: Exact roots and poles
précédent: Exact roots and poles
Table des matières
Index
Roots and poles of a rational function : froot
froot takes a rational function F(x) as argument.
froot returns a vector whose components are the roots and the poles
of F[x], each one followed by it's multiplicity.
If Xcas can not find the exact values of the roots or poles,
it tries to find approximate values if F(x) has numeric coefficients.
Input :
froot((x^5-2*x^4+x^3)/(x-2))
Output :
[1,2,0,3,2,-1]
Hence, for
F(x) = 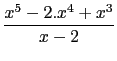 :
:
- 1 is a root of multiplicity 2,
- 0 is a root of multiplicity 3,
- 2 is a pole of order 1.
Input :
froot((x^3-2*x^2+1)/(x-2))
Output :
[1,1,(1+sqrt(5))/2,1,(1-sqrt(5))/2,1,2,-1]
Remark : to have the complex roots and the poles, check Complex in
the cas configuration (red button giving the state line).
Input :
froot((x^2+1)/(x-2))
Output :
[-i,1,i,1,2,-1]
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse
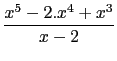 :
: